Emily Savage/The Conversation
In the Middle Ages, most dogs had jobs. In his book Of the Dogsthe 16th-century English physician and scholar John Caius described a hierarchy of dogs, which he classified first and foremost according to their function in human society.
At its apex were specialized hunting dogsincluding greyhounds, known for their “incredible swiftnesse” and bloodhounds, whose powerful sense of smell drove them “through long lanes, crooked reaches, and weary ways” in pursuit of their prey.
But even the “mungrells” that occupied the bottom rungs of the canine social ladder were characterized in terms of their labor or status. For example, as street performers, or turnspits in kitchens – running on wheels that turned roasting meat.

A dog with a spiked collar and a greyhound with a long leash from the Helmingham Herbal and Bestiary (c. 1500). (Yale Centre for British Art, Paul Mellon Collection)
The place of dogs in society changed when hunting became an aristocratic pastime, rather than a necessity. Simultaneously, dogs were welcomed inside noble homes – especially by women. In both cases, dogs were signifiers of elite social rank.
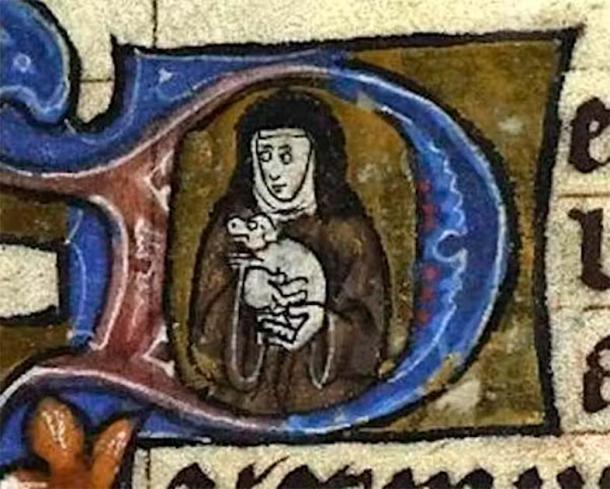
A nun holding her lapdog. (in Stowe MS 17, f. 100r. British Library)
Indeed, in his ranking, Caius positions the “delicate, neate, and pretty” indoor dogs below hunting dogs but above the base mongrels, because of their association with the noble classes. As for puppies: “the smaller they be, the more pleasure they provoke”.
Although the church formally disapproved of pets, clerics themselves often owned dogs. Like women, clerics’ dogs were generally lapdogs, ideally suited to their indoor pursuits.
In Praise of Dogs
Not everyone had such affection for dogs. Concerned about potential violence, urban authorities in England regulated the keeping of guard dogs, as well as violent popular entertainments, such as boar, bear and bull-baiting.
In the Bibledogs are often characterized as filthy scavengers. Proverbs 26:11 famously describes how they return to their own vomit.

A miniature of Sir Lancelot, in conversation with a lady holding a small dog (c. 1315-1325). British Library
On the other hand, the story of St Roch in The Golden Legenda popular 13th century collection of saints’ lives, tells of a dog who carried bread to a starving saint, then healed his wounds by licking them. One of Roch’s saintly attributes, a motif by which viewers can recognize him, is a devoted dog.
The trope of dogs defending their owners or lamenting dead ones can be traced back to the classical period, to texts like Pliny the Elder’s Natural History.
This theme is repeated in the medieval bestiary traditiona moralizing compendium of knowledge about animals both real and mythical. One common story tells of the legendary King Garamantes who, when captured by his enemies, is tracked down and rescued by his faithful dogs. Another tells of a dog who publicly identifies his master’s murderer and attacks him.
The tale of one greyhound, Guinefort, even inspired an unofficial saint’s cult. Writing in the 13th century, Dominican inquisitor and preacher Stephen of Bourbon described a noble family who, falsely believing the dog to have killed their infant, killed Guinefort in retribution.

Detail of a miniature of King Garamantes, being rescued by his dogs, from the Rochester Bestiary (c.1230). (British Library)
Upon discovering the child unharmed (the dog had really saved it from a venomous snake), they honored the “martyred” canine with a proper burial, which led to its veneration and alleged healing miracles. Although Stephen’s story intended to reveal the sin and folly of superstition, it nonetheless underlines what medieval people perceived as the special qualities that distinguished dogs from other animals.
According to the Aberdeen Bestiary (c. 1200):
“No creature is more intelligent than the dog, for dogs have more understanding than other animals; they alone recognize their names and love their masters.”
The association between dogs and loyalty is also expressed in the art of the period, including in relation to marriage. In tomb monuments, depictions of dogs indicate fidelity of a wife to the husband who lies beside her.
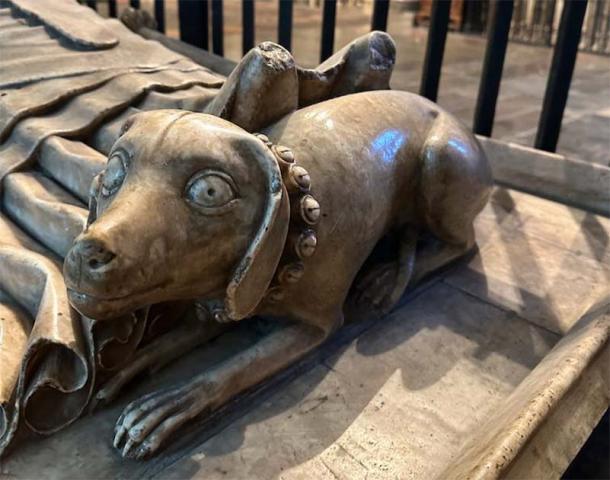

This effigy of a dog is part of Archbishop William Courtenay’s tomb in Trinity Chapel, Canterbury Cathedral. (Author provided, no reuse)
In the case of clerical tombs, however, they may suggest the faith of the deceased, such as Archbishop William Courtenay (d. 1396), buried in Trinity Chapel, Canterbury Cathedral. Courtenay’s alabaster effigy reposes atop a tomb chest on the south side of the chapel. The archbishop wears the robes and miter of his office, and two angels support his cushioned head. A long-eared dog wearing a belled collar lies obediently at his feet.
Although it’s tempting to wonder whether the dog depicted on Courtenay’s tomb may represent an actual pet owned by the archbishop, the belled collar was a popular convention of contemporary iconography, especially for lapdogs.
Pampered Pooches

Allegory of Vanity by Hans Memling (c. 1490). (Museum of Fine Arts of Strasbourg)
Like their modern counterparts, medieval dog owners with means kitted out their companions with a variety of accessories, including leashes, coats and cushions made from fine materials.
Such material investment was central to the aristocratic culture of live nobly (the art of living nobly), where the deliberate consumption of luxury commodities publicly demonstrated one’s status.
Popular perceptions of dog owning and accessorizing also fed gendered stereotypes. Whereas men were more likely to own active dogs for the protection of their life and property, women preferred lapdogs they could cradle and pamper. Toy dogs, then, could also be associated with female idleness and viceas seen in Hans Memling’s painting Allegory of Vanity (c. 1485).
But even working dogs needed meticulous care and attention if they were to perform at their best. A miniature in a lavish 15th-century copy of Gaston Phébus’s influential book Book of Hunting (Book of Hunting) shows kennel attendants examining dogs’ teeth, eyes, and ears – while another bathes the paws of a very good boy.
Top image: Dogs being taken care of in an image from Livre de la Chasse (Book of the Hunt). Source: The Morgan Library and Museum/Faksimile Verlag Luzern
This article was originally published under the title ‘Dogs in the middle ages: what medieval writing tells us about our ancestors’ pets’ by Emily Savage on The Conversationand has been republished under a Creative Commons License.

